Overview
Using BioUML platform you can:- create a project;
- share your project with other users;
- import/export your data to the project folders;
- connect your folders from Dropbox™, Google Drive™ or OneDrive™ as BioUML projects;
- create folders to organize you data and results of they analyses;
- edit and visualize you data on-line using embedded viewers
and editors.
40+ file formats and standards related with biological data are supported; - simulate biological models as well as fit their parameters to correspond experimental data;
- analyze your data using all power of BioUML platform:
- predefined and custom workflows;
- 200+ analyses methods provided by BioUML platform;
- 3-rd party programs integrated via Galaxy platform;
- R scripts;
- Javascript scripts.
Collaborative research
We were inspired by Google tools for collaborative work and have tried to provide similar functionality for collaborative work with biological data.
Main features:- create and share your projects with other users;
- collaborative diagram editing (like Google documents);
- diagram editing history (both session and version);
- built-in group chat.
- BioStore - is the central registry which stores information about user accounts, groups, projects and access rights, as well as information about user's paid subscriptions (databases and services for data analysis).
- BioUML servers stores users data and queries BioStore to check user's login info and get corresponding access rights to these data.
Integration with DropBox™, Google Drive™ and Microsoft OneDrive™



BioUML server will scan all files in connected folder and will try
automatically detect file formats to use corresponding editors/viewers.
For example:
- SBML file will be opened as a diagram, user can edit this diagram as well as start simulation for corresponding model;
- VCF or WIG files can be opened both as table or as track in genome browser.
- to edit and visualize you data on-line using embedded viewers and editors.
40+ file formats and standards related with biological data are supported; - see history of changes;
- simulate biological models as well as fit their parameters to correspond experimental data
- to analyze your data using all power of BioUML platform.
Integration with Git

Version control is a system that records changes to a file or set of files over time so that you can recall specific versions later.
The highest demand on this functionality is requested from systems biologists which develops complex models of biological systems. This process is similar with software development, so it is reasonable to reuse corresponding tools and best practices.
Git project can be cloned on BioUML server as a BioUML project. BioUML project also can be pushed to Git repository. BioUML web interface provides most common actions to work with Git repository:- pull project changes from Git repository to BioUML server;
- commit changes;
- push changes to remote Git repository
- basic actions to work with branches: create branch, switch between branches;
- special pane that shows changes in the project: added, removed or changed files.
For more complicated actions with remote Git repository you can use specialized software. For example GitLab.
Biological databases
Other important feature of BioUML platform is close integration with many biological databases and possibility to present their content as diagrams.Special pane - repository pane shows databases installed on BioUML server and available for a user. Some databases are available for free, for access to commercial databases you need to by corresponding subscription via BioStore.
Diagrams
BioUML allows present information Information from many biological databases can be presented as diagram.Solitaire game
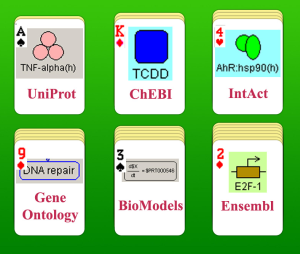
- the desk – a BioUML diagram;
- packs of cards – different biological databases (for example, Ensembl, UniProt, ChEBI, etc);
- cards – biological objects (genes, proteins, lipids, etc.);
- solitaire game – reconstructed biological pathway.
- different databases – “packs of cards” - (Ensembl, UniProt, ChEBI, IntAct, GeneOntology, Reactome, BioModels) can be installed BioUML servers;
- when user add some component on a diagram he can select from which database corresponding biological object will be selected;
- full text search engine allows to search information in different databases for specified biological object type (gene, protein, etc.) using several corresponding database simultaneously. Then user can select one or more found objects and put them on diagram;
- graph search engine allows to find biologically related objects (participating in the same reaction or semantic relation) in the databases and put them into diagram.